URL slug: Definition & best practices defined for SEO success

Crafting friendly URLs holds utmost importance, as they directly influence a website’s search engine ranking, click-through rates, and overall user experience.
A clean, keyword-rich slug not only makes your links easier to read and remember, but also signals relevance to search engines.
Even when using a link shortener, the custom URL slug you choose plays a vital role in branding, trust-building, and improving link performance.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best practices for structuring slugs that are SEO-friendly, user-focused, and optimized to work seamlessly across platforms and tools.
So, let’s get started!
What is a URL slug?
The portion of a URL that follows the domain name and any subdirectories is known as the “URL slug”. It is a human-readable and user-friendly text used to designate a particular web page.
Keywords associated with the page’s content are frequently used in URL slugs, making them more descriptive and much easier to remember.

URL slug etymology
The term “slug” in the context of publishing goes back to the days of print journalism. In newsrooms, a slug was a short label or nickname given internally to an article as it moved through the editing and production workflow.
In web publishing, that sense of a brief identifier carried over, and a slug became the short, human-readable token for a page.
Why is it called a URL slug?
In digital contexts and web systems, it’s called a URL slug because it provides a concise, human-readable identifier for a web page. Besides, it follows the domain and subdirectories, making URLs memorable and SEO-friendly.
Why are URL slugs important for SEO?
URL slugs are vital for SEO as they provide a concise, descriptive, and user-friendly representation of a webpage’s content. This helps both search engines and visitors quickly understand your pages.
Moreover, the following points highlight why well-crafted slugs are essential:
- Boost search rankings: A concise, keyword-rich slug signals relevance to search engines and can improve your page’s visibility.
- Enhance user experience: Clean and descriptive slugs help visitors instantly understand what the page is about before clicking.
- Improve readability: Short, well-structured URLs are easier to read, remember, and share across platforms.
- Increase trust and CTR: Clear slugs look more professional, which builds trust and encourages higher click-through rates.
- Support better indexing: Search engines can crawl and categorize content more effectively when slugs are structured properly.
- Encourage backlinks: Shareable, meaningful URLs are more likely to be cited or linked to by other websites.
URL slug best practices: Best tips for writing SEO-friendly slugs
People often think URL slugs are a minor SEO element, but that’s not true. They can significantly impact your website’s performance in search engine rankings and enhance user engagement.
Creating SEO-friendly URLs with refined slugs involves careful consideration of keywords, readability, and user experience. Below are some key actionable tips to help you optimize your URL slugs effectively.
1. Include your keyword in the URL slug
The very first object that comes to mind when discussing SEO is the “keyword”. In addition to the content, you must include your primary keyword in the URL slugs as well.
Search engines use slugs to understand the context of your page content. As far as users are concerned, looking at the URL makes it easier for them to identify what the specific page is really about.
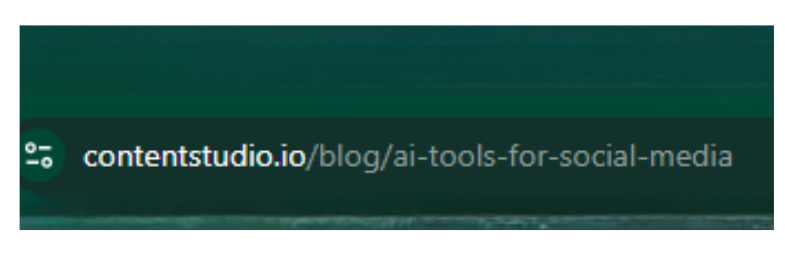
For example, if your focus keyword is ‘AI Tools for Social Media’, you need to incorporate these keywords in your URL slug, just like ContentStudio did.
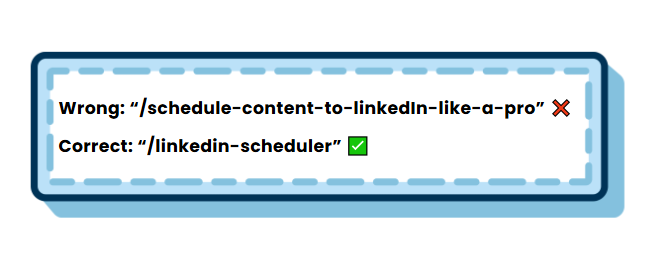
2. Keep the slug part short, yet informative
Try to keep your URL slugs short and informative to make them appealing to both users and search engines. Imagine you run a website dedicated to a content curation tool. Instead of having lengthy URL slugs like:

Consider using a more compact and descriptive URL slug:

This shorter version conveys the essence of the page’s content while being more SEO and user-friendly.
Note: Users are more likely to click on links with concise and relevant URLs, as they can quickly grasp the page’s content before visiting it. Moreover, shareability improves when URLs are shorter, making it easier for people to share your content on other platforms hassle-free.
3. Use hyphens, not underscores, to separate words
Prioritize the use of hyphens instead of underscores. Hyphens serve as clear word separators that enhance the visual appeal and readability of your URLs.
Search engines recognize hyphens as natural dividers between words. This enables them to interpret the content more accurately.
Consider the following two URL slugs:
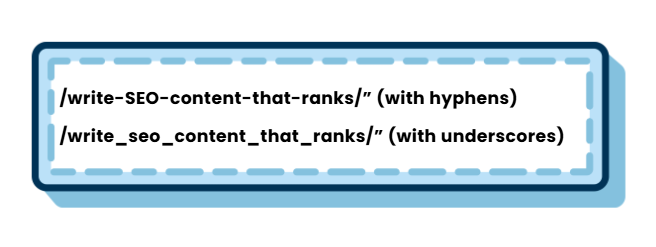
Visibly, the first version presents a tidy and simple URL that users and search engines can process without difficulty. The second version with underscores, on the other hand, seems cluttered and less practical.
4. Use lowercase letters in the URL slug
To ensure consistency and avoid problems with duplicate content, always use lowercase letters and characters when creating your page slug.
Instead of something like “What-Are-Ctas-In-Marketing,” “what-are-ctas-in-marketing” is preferred.
Note: URLs are handled case-sensitively by search engines.
This means that “what-are-ctas-in-marketing” and “What-Are-Ctas-In-Marketing” are treated as two separate URLs. This might result in issues with identical content and weaken your website’s SEO efforts.
Moreover, mixed-case URLs can make it more difficult for users to remember or share them correctly.
5. Keep it evergreen
Use content that will remain relevant and valuable over time when creating URL slugs. More precisely, avoid incorporating time-sensitive details such as specific years or dates in your URL slugs.
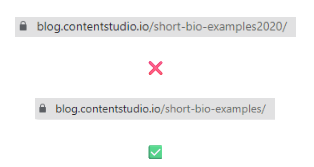
Evergreen slugs help improve SEO results because search engines value content that holds its value over an extended period.
You can prevent potential broken links and maintain the SEO authority that has developed over time by removing time-sensitive elements from your slugs. This eliminates the need to update URLs with each passing year.
6. Use one domain and one subdomain
Maintain a clean URL structure by sticking to one primary domain and a minimal number of subdomains (stick to 1). This approach helps strengthen your website’s authority and assists with content fragmentation.
Opt for “blog.example.com” instead of “example.com/blog.”
Moreover, a compact URL structure simplifies your website’s maintenance and improves link equity distribution. You avoid the risk of diluting SEO authority across multiple subdomains, ensuring that your primary domain gains maximum value from incoming links.
Note: You can use subfolders instead of subdomains. Subfolders within the main domain consolidate link equity, making the website more authoritative and easier to rank. Many case studies have shown significant traffic increases when moving content from subdomains to subfolders.
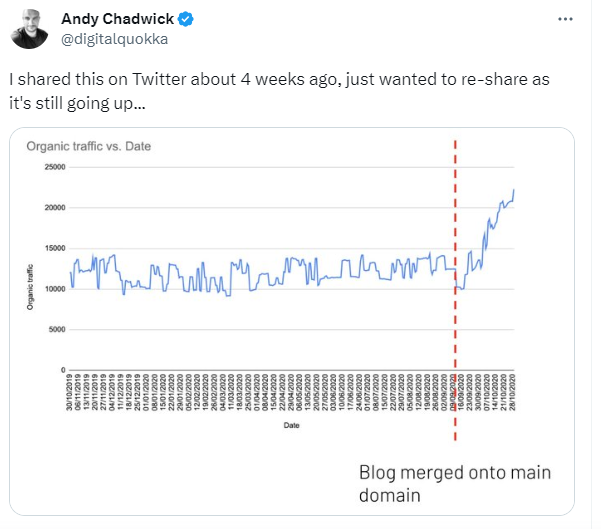
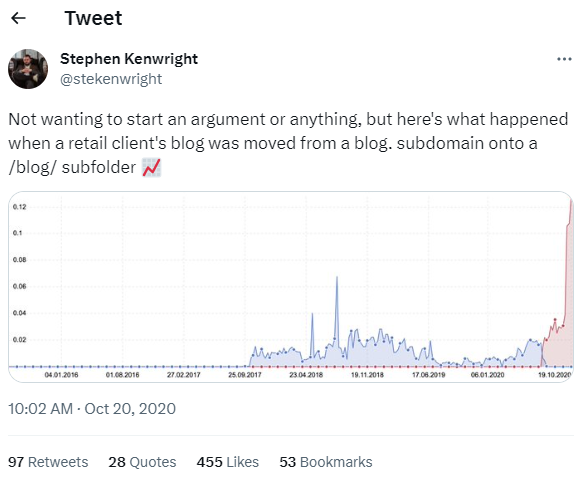
7. Update old slugs, but be careful
Always ensure that proper redirects are set up when changing a slug to prevent broken links and maintain the SEO authority of the previous URL.
Because sudden changes can result in broken links and negatively affect user experience and search engine rankings, managing URL changes requires careful planning.
You can smoothly direct users and search engines to the new URL while transferring the SEO value accrued by the old slug by implementing “301 redirects”.
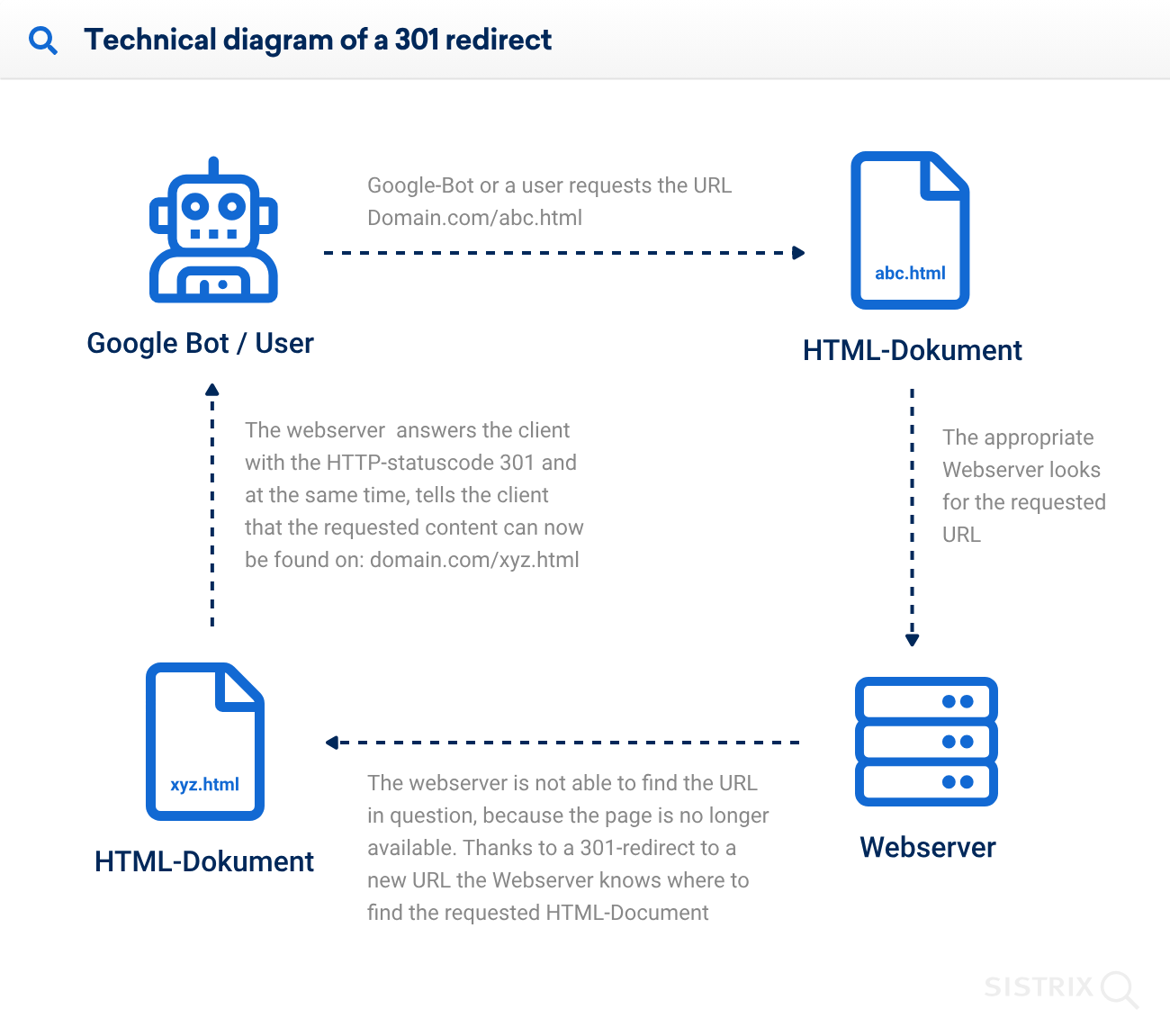
Your website will continue to be user-friendly and search engine optimized if outdated slugs are strategically updated.
Furthermore, it aids in maintaining backlinks and search engine rankings while securing a steady flow of organic traffic to your updated content.
8. Match slugs to headlines
To further emphasize the relevance of your content, you must confirm that your URL slugs and page headlines are consistent. Both users and search engines will have an easier time understanding the purpose of your page if you align both elements.
This practice assists search engines in associating your content’s main topic with the URL, potentially improving your website’s ranking for relevant search queries.
Additionally, users are more likely to click on links that display a clear correlation between the headline and URL, enhancing their browsing experience.
9. Use fewer page categories
Keep your URL slug structure simple by minimizing the number of categories and avoiding keyword stuffing. Clear and uncomplicated slugs make it easier for users to navigate your website and for search engines to understand your content.
Let’s take a look at a social media analytics tool web page. Rather than using a confusing, long URL, they preferred a short and descriptive URL slug:
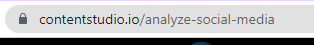
This direct method keeps things crystal clear.
10. Choose a memorable domain name
Find a unique domain name and pair it with a relevant URL slug. By doing this, you can enhance your band’s recognition and reinforce your website’s theme.
The combination in the picture above exemplifies how a cohesive URL structure can align with your brand’s identity.
Note: When users encounter a domain name that resonates with their interests, they are more likely to remember and revisit your website. This instant recall plays a significant role in building a loyal audience base.
Adding a relevant URL slug like further enhances user engagement. It communicates the content focus, guiding visitors to the specific section they are interested in. This targeted approach saves users time and effort, promoting a positive user experience.
Also Read:Beginners’ guide to URLs: URL types, structure & best practices
How to change URL slug in WordPress?
WordPress is known for its user-friendly interface and flexibility, making it a popular choice for website development. Changing a URL slug on WordPress is a simple process that can be done within the platform’s settings by following the steps below.
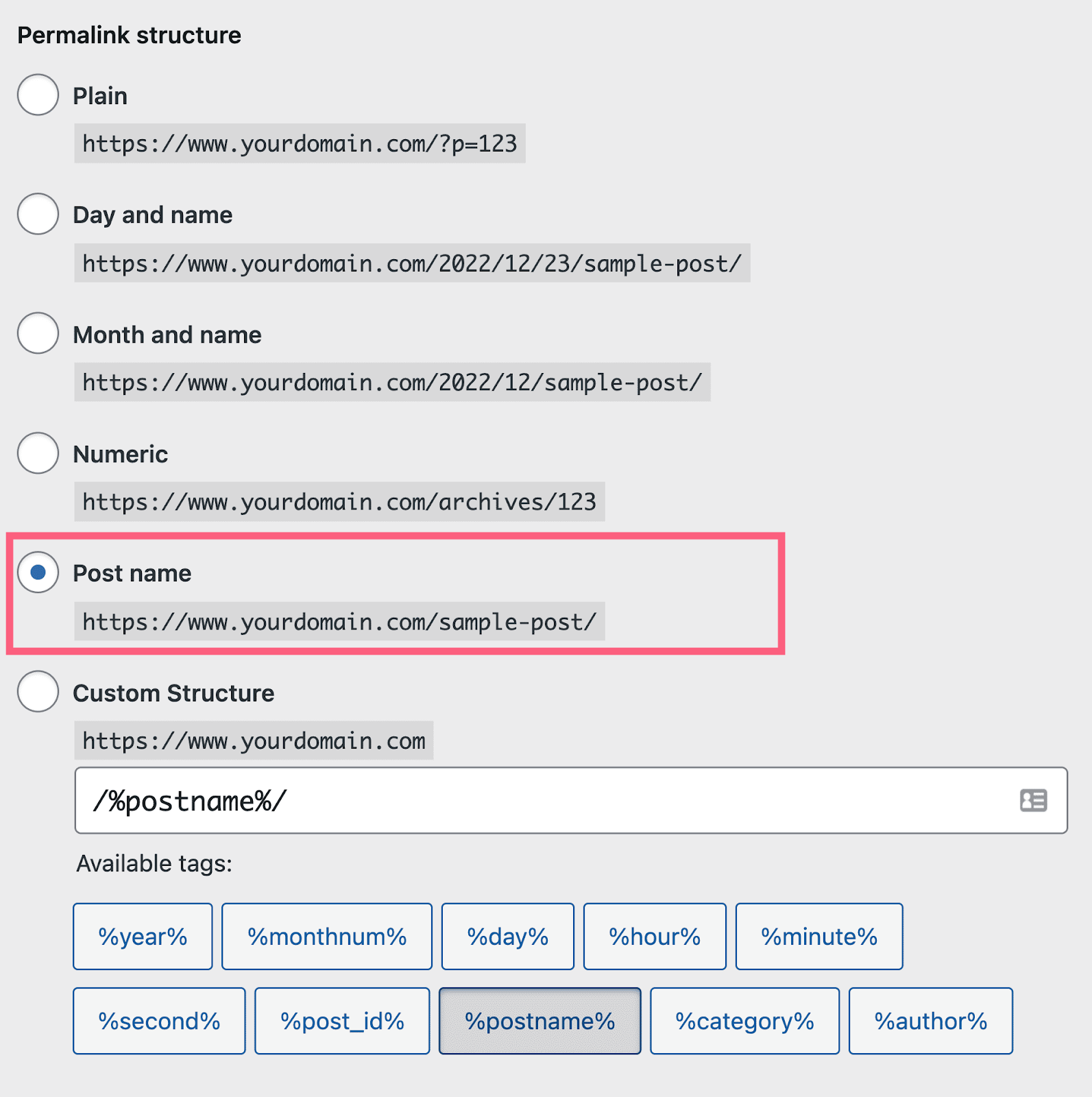
Step 1: Set up your permalink structure
Before starting, you must ensure that your permalink structure allows for user-friendly URL slugs. Navigate to “Settings” and then to “Permalinks.”
You can choose one of the standard permalink structure types or create your own. However, it is recommended to use the “Post name” structure.
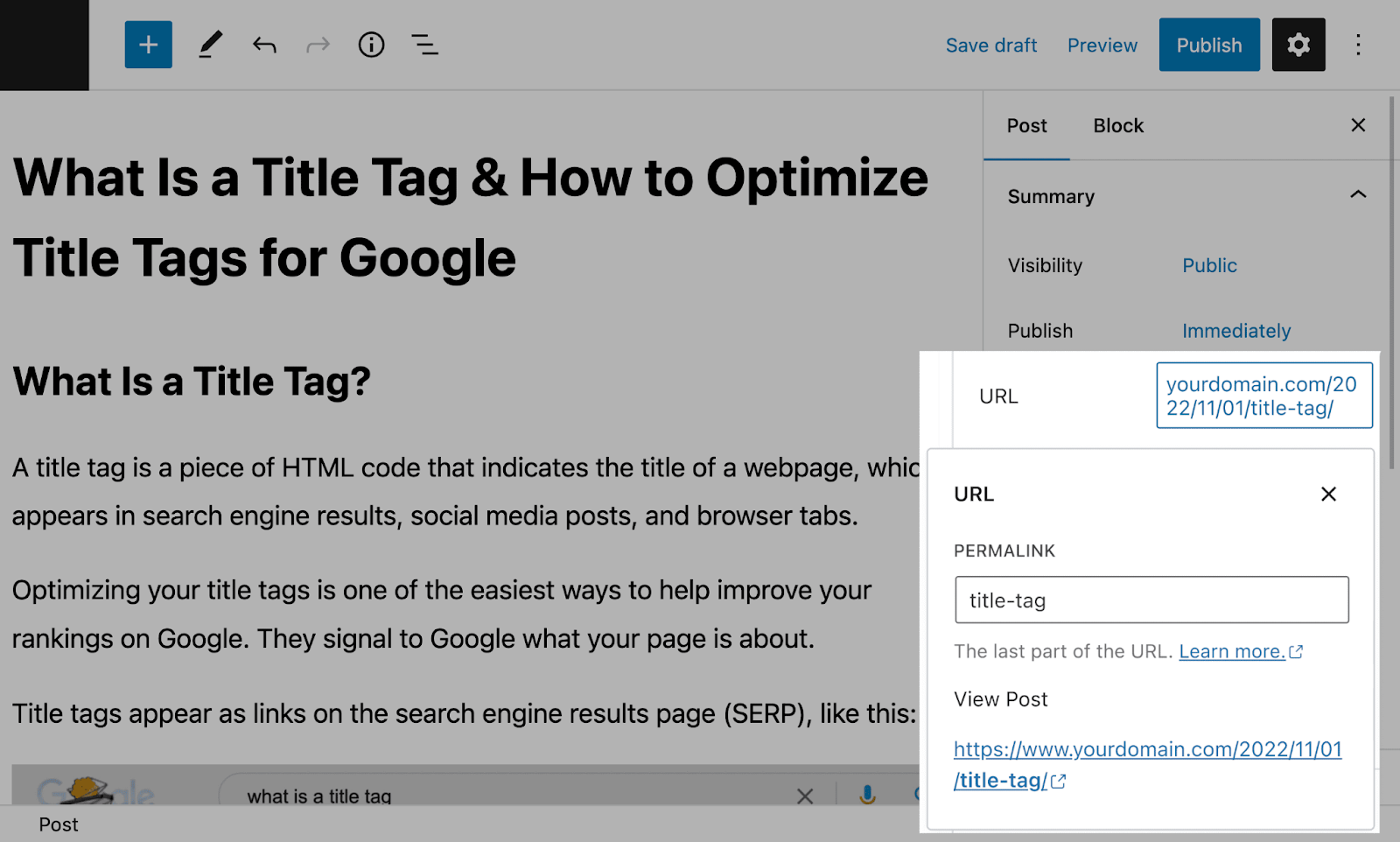
Step 2: Edit the slug in the post or page editor
Open the editor of the post or webpage and look for the “URL” section in the rightmost panel. Click on the automatically generated slug and edit it the way you want to. That’s it.
Related: How to Change Permalink in WordPress: Step-by-Step
Benefits of using SEO-friendly URL slugs
An SEO-friendly URL slug is more than just aesthetic; it helps both users and search engines understand what a page is about before even clicking. The right structure can improve visibility, credibility, and usability across the board.
1. Enhanced search engine visibility
Strengthening your website’s search engine optimization is a key advantage of using SEO-friendly URL slugs. Search engines can learn a lot about the content of your page when you use relevant keywords in the URL slugs of your URLs.
The search engine’s ability to index and rank your pages for relevant search queries is subsequently improved.
2. Amplified shareability
Concise, descriptive, and simple-to-remember URLs are more likely to be shared on various platforms. There is a much greater chance for users to share valuable content with their friends, coworkers, or social media networks when the URLs are simple and clear.
When the reader comes across your URL slug, which is to the point (has the focus keyword), they can easily copy and paste the URL, knowing that the link is authentic. The user-friendly and shareable URL slug allows others to access the same content quickly and effortlessly.
3. Higher click-through rates
An SEO-optimized URL slug can also improve click-through rates (CTR) from search engine results pages (SERPs). When users see a relevant and well-structured URL slug that matches their search intent, they are more likely to click on the link, expecting it to lead to content that aligns with their needs.
The user-friendly and keyword-rich URL slug assures the user that the page contains the desired information, thus increasing the likelihood of a click.
Let’s say someone is searching for “best smartphone deals”. He’ll click on a URL with a slug like “/best-smartphone-deals” rather than a generic one like “/products/abc123.”
6 major mistakes to avoid while creating URL Slugs
As discussed before, URL slugs play an essential role in enhancing your website’s SEO and user experience. However, there are common mistakes that can impact your website’s performance and rankings.
Below are six prominent errors that you need to avoid when crafting URL slugs for your web pages.
1. Avoid stop words
Common words like “and,” “the,” “of,” “a”, etc., are stop words, and they add very little to the meaning of a URL. Avoid using them in your slugs because doing so will lengthen them and make them less readable.
For example:
2. Avoid using dates in slugs
The use of specific dates in URL slugs can result in out-of-date content and affect SEO. Rather than
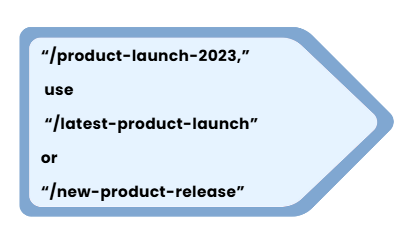
In this manner, you can prevent updating your URLs annually and ensure their continued relevance.
The biggest issue is that when you need to change the date from 2025 to 2026, you must update the slug and redirect the old URL to the new one. This process can be time-consuming and may lead to broken links if not handled correctly.
Moreover, these URL redirects can be suboptimal. They may result in less link juice passing through to the destination URLs. This means that the SEO value of your old URL might not fully transfer to the new one.
Note: By leaving out numbers and using descriptive slugs, you avoid the need for frequent redirects and maintain a consistent flow of link equity to your content.
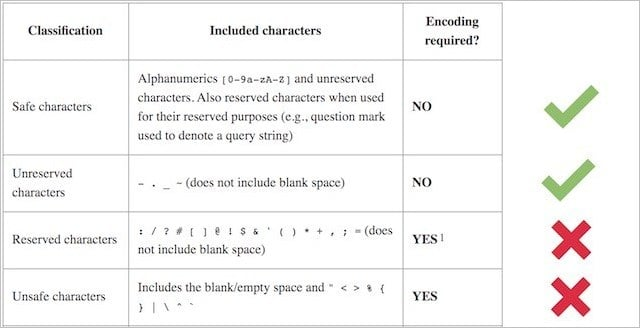
3. Avoid using special characters
Including special characters like question marks, exclamation marks, or dollar signs can cause issues with URL encoding in your slugs.
Certain characters are replaced with encoded strings, making the URL less readable. Furthermore, some special characters may not be universally supported by all browsers and platforms, potentially causing compatibility issues for some users.
What’s best is that you can use hyphens to separate words in your slugs. Hyphens are considered word separators, providing better readability for search engines and users alike. Hyphen-separated slugs contribute to a cleaner and more professional appearance for your URLs.
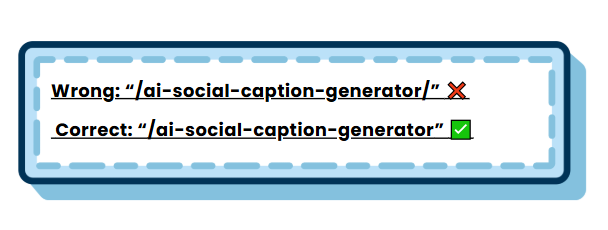
4. Avoid trailing slash issues
Adding a trailing slash at the end of a URL can unintentionally create duplicate content problems for your website.
A negative effect on SEO may result from search engines treating URLs with and without the trailing slash as separate pages. Maintaining consistency in your URL structure is essential for mitigating this problem.
You can guarantee that users and search engines always access the preferred version of your content by consistently using one format for your URLs and implementing the appropriate redirects.
For example:
5. Avoid broken links after making any changes
Making changes to your URL structure or slugs is a common practice, but it’s critical to handle these changes carefully. This is to avoid broken links and maintain a consistent user experience.
Note: Setting up 301 redirects from the old URLs to the new ones is essential when changing a URL.
Users who are trying to access your content may become frustrated if you neglect to implement proper redirects. Broken links not only have a bad effect on the user experience, but they also give the wrong impression to search engines, which could lower the ranking of your website.
6. Avoid ranking cannibalization
Ranking or keyword cannibalization is a phenomenon where multiple pages on your website compete for the same keyword. As a result, there is internal competition in the search results.
Concentrate on making sure that each URL slug targets a different and specific keyword or topic to prevent this phenomenon. Conduct keyword research and use different variations for each page.
Note: You can improve each page’s content clarity and relevance in the eyes of search engines by allocating unique URLs to particular keywords or topics. This enables search algorithms to better understand the purpose and intent of your pages, leading to improved rankings for relevant search queries.
Concluding remarks
From understanding what a URL slug is to learning why it matters for SEO, user experience, and CTR, this guide covered everything you need to know about crafting the perfect slug.
We explored best practices like keeping slugs short, keyword-rich, and evergreen, while also avoiding common mistakes such as using dates, special characters, or stop words.
At the end of the day, an optimized and clean URL slug does more than make your URL look professional. It builds trust, strengthens branding, improves visibility, and drives clicks. Treat your slugs as a small but powerful SEO asset, and they’ll continue to pay off in the long run.
Ready to put your optimized slugs into action?
Try Replug.io! It is the ultimate link shortener and URL optimization tool that helps you create clean, branded, and trackable links in seconds. Give it a go today!
Frequently asked questions
What is the optimal URL slug length?
The optimal URL slug length is typically 3-5 words or 20-60 characters, ensuring it’s concise, descriptive, and includes relevant keywords for SEO. Shorter slugs are user-friendly and easier to share, while avoiding excessive length improves readability and search engine performance.
What is an example of a slug?
An example of a URL slug is “best-hiking-trails” in the URL “www.example.com/blog/best-hiking-trails”.
URL slug examples like this are short, descriptive, and use keywords to clearly indicate the page’s content, enhancing SEO and user experience.
How to create a slug?
To create a slug, manually craft a concise, descriptive phrase using lowercase letters, hyphens, and relevant keywords, like “best-travel-tips” for a blog post. Alternatively, use a URL slug generator tool to automatically produce SEO-friendly slugs based on your page title or content. Both methods certify user-friendly and search-optimized URLs.
What is the difference between URL slug and path?
A URL slug is the specific, human-readable part of a URL that identifies a page, like “about-us” in “www.example.com/about-us”. In contrast, the URL path includes the slug and any preceding directories, such as “/blog/about-us”.
Understanding the difference between URL slug vs. path helps clarify that the slug is a concise page identifier, while the path shows the full navigational structure.
What is the difference between a permalink and a URL slug?
A URL slug is the descriptive, human-readable segment of a URL identifying a specific page, like “contact-us” in “www.example.com/contact-us”. A permalink is the complete, permanent URL, including the domain, directories, and slug, designed to remain unchanged. This distinction in permalink vs URL slug ensures clarity in linking and SEO optimization.
What is the difference between a URL slug and a URL?
A URL slug is the specific, human-readable part of a URL that identifies a particular page, such as “blog-post” in “www.example.com/blog-post”. On the other hand, a URL is the complete web address, including the domain, protocol, and path, like “https://www.example.com/blog-post”. Understanding this difference clarifies that the slug is just one component of the whole URL structure.
Does changing the slug change the URL?
Yes, changing the URL slug alters the URL, as the slug is the part that identifies a specific page, like “new-post” in “www.example.com/new-post”. Modifying it, for instance, to “updated-post”, results in a new URL, “www.example.com/updated-post”, which may impact SEO and require redirects to avoid broken links.
What are URL slug parameters?
URL slug parameters are not typically part of a slug, as slugs are static, human-readable URL segments like “product-name” in “www.example.com/product-name”. URL parameters, appended after a slug (e.g., “?id=123” in “www.example.com/product-name?id=123”), are dynamic query strings used to pass additional data to a webpage. Understanding this distinction ensures clarity in URL structure and functionality.